Sample Undergraduate Applied Strategy Report
Here is a sample that showcases why we are one of the world’s leading academic writing firms. This assignment was created by one of our expert academic writers and demonstrated the highest academic quality. Place your order today to achieve academic greatness.
Applied Corporate Strategy Assessment: Strategic Analysis Report Vodafone
Executive summary
Vodafone has operated in the UK telecommunication sector that has recently decided to acquire European Liberty. The external environment of the telecommunication sector would help the management to frame future decisions. The operational cost of the companies would be raised because of the current pandemic. All kinds of business sectors including the telecommunication industry have faced a couple of operation issues while performing the business. The organisation faces threats from the competitors along with the substitute the strength of the company is in its workforce and capability of cost reduction. Vodafone would be able to overcome the weakness of standard network infrastructure along with competition through the acquisition of Liberty Global. The corporate strategy of acquisition for Vodafone is acceptable to the employees and the investors.
Introduction
Vodafone is a multinational telecommunications company based in the UK (Corporate, 2019). Vodafone operates in the telecommunications industry of the UK and has recently acquired European Liberty. The telecommunications sector of the UK had a GVA of £30.2 billion in 2015 and contributed significantly to the national GDP (Parliament, 2018). Vodafone acquired European Liberty Global in July 2019 for a value of €18.4 billion (Morningstar, 2019). This strategic analysis report details the corporate strategy of Vodafone and evaluates the external and internal environment of the firm.
External analysis
PESTEL Analysis
The PESTEL analysis is conducted to evaluate the external environment of the telecommunications industry in the UK.
Political factors-
UK government is quite aware of the political issues of the countries, where addressing deteriorating economic conditions may provide enough feasibility and stability to the government (BBC, 2020). The telecommunication industry of the UK plays a major role in the stability of the country’s economy. After Brexit, the UK becomes politically independent regarding any business decision-making (BBC, 2019). Such initiation assists the government to control any kind of political issues during merging and acquisitions in the business and it is beneficial for the companies also to operate due to lower taxation. However, the firm has been operating in multiple countries. Vodafone acquires European Liberty, which generally operates telecommunication businesses in Germany, the Czech Republic and other EU countries. The political stability of the UK government may offer opportunities to Vodafone in case of expand its telecommunication business over other EU countries through the acquired company.
Economic factors-
The UK holds a stable economic condition and preferred to be one of the most stable in the world. Here the economic status may include different factors such as GDP, inflation rate, unemployment rate, devaluations, and others. The economic trend of the UK may indicate the possibilities for the telecommunication sectors to be expanded in a better way. It seems that the GDP of the UK has increased by 1.4% from 2018 to 2019. As per Appendix 1, the inflation rate also decreased by 0.5% which has indicated massive turnover and success in retaining the economy (Theguardian, 2020). Here 80% of total GDP comes from the service-oriented business, which indicates a better chance for the telecommunication sectors (Appendix 2). The operational cost of the companies would also be enhanced by a slight portion due to the current pandemic (FinancialTimes, 2019). The certain stable economic condition of the UK may assist Vodafone in investing more in terms of merging and acquisition. Such acquisition of Vodafone may show possible opportunities in terms of more economical gain.
Social Factors-
Social factors of the UK include its citizens, lifestyle, health issues, education, and level of income. Although the UK has a rich culture, where most of the people have income more than the poverty level and the educational and other systems are quite advanced. Even after all those factors, the recent pandemic situation of Covid-19 has disrupted all the lifestyles of the country (Jolley & Paterson, 2020). It results in huge mortality, economical degradation, and others. All kinds of business sectors including telecommunication sectors also faced huge issues in the operation of their regular business. Recent situations affect the business over Vodafone, as all the prime locations of its business get affected and continuing service becomes challenging over such areas, which can be considered as a real threat.
Technological factors-
The UK holds one of the most advanced and stable telecommunication infrastructures in the entire world. Lots of major telecommunication organizations operate their service globally from here. The service becomes more technology-based, where organizations are capable enough to evolve with the changes and handles any kind of situation. In the recent period of the Covid-19 pandemic, where social gatherings and the traditional educational system have been disrupted, peoples and organizations prefer more on the telecom industries for internet services as the work-from-home concept can be maintained in other industries (BBC, 2020). The acquisition of European Liberty by Vodafone provides a wider business market, and the demand for network services during the Covid-19 situation shows positive opportunities for the organization in terms of high service demand.
Legal factors-
Legal factors are assigned in every activity of telecommunication organizations. The UK holds certain legislation and legal framework for telecommunication organizations differently for internal and external organizations. Companies Act (2006) assigns quite a basic legislation for operating business in the UK (Legislation.gov.uk, 2020). On the other hand, the UK’s general public M&A framework also assigns the companies for merging and acquisitions. The companies need to be incorporated with the Communications Act (2003). Additionally, one telecom company in the UK may have to pay different taxes differently for doing business in foreign countries. Vodafone may have to pay quite more taxation for the acquisition of European Liberty in both the home market and foreign markets. Such enhancement in tax-paying can be considered a threat.
Environmental factors-
Telecommunication sectors have a bad impact on the environment. High demand for telecom services in the UK may disrupt environmental conditions. Emitting radiation and high frequency for high demand may hamper the ecological system of the region (Russell, 2018). Additionally, such an industry hurts human health and trees. The growing number of telecom organizations in the UK may raise different kinds of environmental issues. Vodafone also contributes to environmental degradation through its telecom service which has ensured the following sustainability concern. Expansion of business may hamper the environment more, which is a serious threat issue to mankind and the environment.
Receive feedback on language, structure and layout
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Grammar
- Style consistency

Porter’s five forces
Porter’s five forces analysis has been done to determine the industry attractiveness and competitive rivalry in the telecommunications sector of the UK.
Bargaining power of the buyers:
The bargaining power of the consumers of the telecommunications industry of the UK is high. The higher amount of regulation in the industry results in intense competition among the market drivers regarding pricing and services (David, 2011). The customers have the scope of influencing the prices of the services that are offered by the telecom companies. The bargaining power is high for the buyers due to the high level of concentration and availability of switching at a low cost. There is a similar margin and cost structure of operations among the players in the industry.
Bargaining power of the suppliers:
The bargaining power of the suppliers is high in the telecommunications industry of the UK due to the unavailability of substitutes. The network sharing equipment and network spectrum support services provided by the suppliers are costly due to the high cost of switching along with the availability of the suppliers in other markets. The companies in this sector have to pay higher than market rates to the suppliers due to the strategic importance of the supply.
The threat of substitutes:
Substitute goods pose a moderate threat in the telecom industry as the consumers have the opportunity to switch easily to specialised service providers for internet services and television networks. Despite the wider convenience of using the services of the telecom operators, the customers are often attracted to those substitutes which are easy to obtain from the local dealers for the television network and internet connection and at lower rates (Vodafone, 2020). The presence of substitutes can affect the industry’s attractiveness as the customers can suffice their needs with similar products and services at lower prices.
The threat of new entrants:
The threat of new entrants is low in the telecom industry of the UK due to the requirement of high capital investment for setting up telecom operations. Additionally, the companies already present in the market can benefit from the economics of scale and cost advantages. The high initial investment reduces the market attractiveness for the new entrants, as the customers are already loyal to the present brands. The political and administrative dimensions of the telecom industry also discourage new entrants.
Competitive rivalry:
There is high competitive rivalry in the telecom industry due to the presence of numerous competitors and the availability of numerous consumers forming a monopolistic competition. There are multiple organisations offering telecom services in the UK like O2, Vodafone, British telecom etc. in the sector (Parliament, 2018). The high intensity of competition presents a threat for Vodafone as the rival firms use strategies related to price and non-price for gaining a competitive advantage. The budgetary allocation of the rival organisations for marketing and promotions also determines the attractiveness of the industry.
Internal analysis
Resources
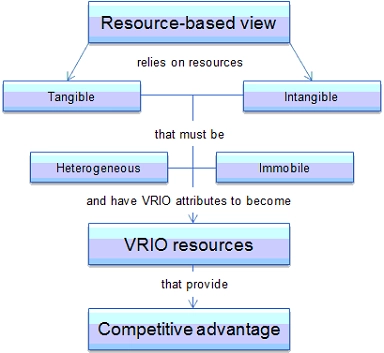
Considering Appendix 3, the tangible resources of Vodafone include the physical resources of the organisation, which includes more than 400 stores across the UK (Corporate, 2019). The company can deliver fast and efficient services through its well-connected stores across the country. This is a strength of Vodafone.
Vodafone offers a variety of services to consumers in the UK comprising cellular data along with broadband and mobile communication networks across the 3G and 4G spectrums (Corporate, 2019). The company also offers a 30 days service guarantee to the consumers as it is confident in the quality of service and customer satisfaction. This is an opportunity for the company to gain a competitive advantage and increase sales.
The network infrastructure of Vodafone is another tangible asset of the organisation as the company offers fixed voice and mobile services to the consumers along with data services (Vodafone, 2010). The network infrastructure of the company includes second-generation and third-generation networks along with high-speed packet access technology, which increases the speed of data transmission for the customers. Similar infrastructure is available with the competitors and hence it is a weakness for the company.
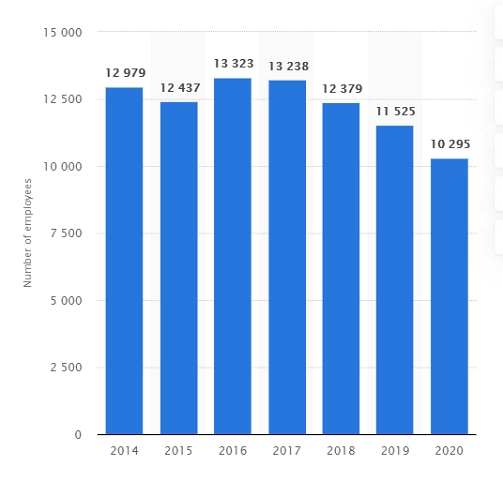
People or the human resources of Vodafone are the intangible resources of the organisation. Vodafone employs 10,295 employees as in Appendix 4, which allows the company to offer seamless services to the customers (Statista, 2020). This is a strength for the company as people form an intangible resource that cannot be replicated by the competitors.
The IT technologies of Vodafone offer them an opportunity to leverage their intellectual property for leveraging cloud-based facilities. The intangible asset allows the organisation to expand its processing abilities and offer more revenue-generating services through cloud-oriented architecture solutions. This is a strength for the company as it enhances the experience of the users.
Competencies
Porters Value Chain
| Distinctive competencies | Value chain activity |
| Cost reduction | Operations |
| Delivery of the best customer experience | Marketing and Sales |
| Evolving the networks | Service |
| More opportunities for the employees | Human resource management |
| Research and development | Technological development |
Cost reduction is a distinctive competency of Vodafone, which has enabled the company to enhance the quality of operations as the organisation has started infrastructure sharing with 70% radio sites along with the transmission with self-build infrastructure (Vodafone, 2010). These initiatives of the organisation along with information technology transformation have enhanced the operational efficiency of the telecom firm. The initiative of delivering the best customer service is a valuable marketing and sales activity in the value chain of Vodafone. The organisation intends to offer seamless service to the customers and market them the telephone and internet services along with a 30-day satisfaction guarantee (Vodafone, 2010). Vodafone has the competency of continuously evolving their networks by achieving a hundred per cent coverage with their 3G and 4G infrastructure along with providing high broadband speeds (David, 2011). The organisation has been able to perform significantly well in the service activity of the value chain through the transmission network evaluation activities for making the infrastructure scalable and cost-effective.
The organisation has provided more opportunities for the employees of Liberty Global to be a part of a global Challenger in the Telco segments (IBC, 2019). This suffices the human resource management aspect of the value chain as Vodafone has provided more opportunities to its staff for representing the organisation at the international and comparative levels (Ambrosini, et al., 2015). Research and development is a distinctive competency of Vodafone as the organisation has spent a significant portion of their profits on the development of new and innovative technologies. Vodafone has invested heavily in solar panels for powering its base stations in the UK along with focusing on incremental commercial enhancements (Vodafone, 2010). The organisation has been able to accomplish the technological development activity of the value chain by conducting and achieving successful trials of the 5G spectrum along with specialising in near field communications.
VRIO analysis
| Distinctive competencies | Valuable | Rare | Inimitability | Organised | Competitive Advantage |
| Cost reduction | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Sustainable competitive advantage |
| Delivery of the best customer experience | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Unused competitive advantage |
| Evolving the networks | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Unused competitive advantage |
| More opportunities for the employees | Yes | No | No | Yes | Competitive parity |
| Research and development | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Sustainable competitive advantage |
The VRIO analysis suggests that Vodafone has an unused competitive advantage in the telecommunications market of the UK. The company has a sustainable competitive advantage due to the distinct competency of cost reduction and research and development (Ambrosini, et al., 2015). The unused competitive advantage for the company rangers in the category of delivering the best customer experience along with evolving their networks, as both are not difficult to imitate by the competitors (Corporate, 2019). The organisation, however, lacks in providing more opportunities to the employees.
Vodafone has the core competency of being able to achieve cost reduction in its operations, which provides a sustainable competitive advantage to the organisation. The company has the strength of cost reduction as it has undertaken its transformation in the business, which has allowed the customers to have a simplified access experience to the applications (Vodafone, 2010). The organisation is also able to leverage the audio and video conferencing facilities, which have been improved through the integration of cloud infrastructure. Having control over the cost base has enabled the organisation to introduce relaxation in the pricing of its data and television network services for the customers which eventually has resulted in a surge in the customer base. The company also owns more than 76% of the transmission network in Europe, which enables them to reduce costs and earn revenues by allowing other telecom operators to use a part of their infrastructure, thereby gaining a competitive advantage (Vodafone, 2010).
Strategy evaluation
Vodafone had undertaken the strategy of acquisition of Europa Liberty Global to expand the scale of operations and achieve a competitive advantage by gaining access to a larger customer base in Germany, the Netherlands, Austria etc. along with other countries (Theguardian, 2018).
SAFe test
Suitability:
TOWS
| Internal factors | |||
| External factors | Strengths | Weaknesses | |
| Opportunities | Tangible resources of 400 stores in the UK can be used to leverage the opportunity of affordability of the staff (Vodafone, 2010).
10,295 employees can be used to offer seamless service to consumers during COVID-19. IT technologies can be used to capitalising the opportunity of expansion with government support. Cost reduction strength can be used to acquire similar companies to increase market reach. |
The weakness of having an average network infrastructure of Vodafone can be overcome with the opportunity of leveraging the scope of expansion of infrastructure reach (Corporate, 2019). | |
| Threats | The strength of 400 stores of the company can mitigate the threat of opening personalised services to the customers during COVID-19 so that the clients do not have to travel too much.
IT technologies and innovation can scale the business and avoid the threat of high taxes (Ambrosini, et al., 2015). The threat of substitutes can be overcome with the strength of the workforce to offer seamless service. |
The weakness of similar network infrastructure can be minimised by the expansion of the network through acquisition (David, 2011). The threat of substitution can be avoided through the best quality customer service and by reducing costs. | |
The corporate strategy of acquisition for Vodafone has been developed based on the organisational strength of having a formidable workforce and the availability of IT technologies for capitalising on the scope of expanding the customer base (Ambrosini, et al., 2015). The opportunity of gaining access to new markets in Germany and the Netherlands has been capitalised based on the strength of cost reduction of the company as it would be able to recover the cost of investment very easily.
Acceptability:
Stakeholder Power/Interest matrix
| Monitor
Suppliers |
Keep informed
Regulatory authorities |
| Keep satisfied
Customers Investors |
Key players
Employees |
The five stakeholder groups that have been identified for Vodafone are customers, regulatory authorities, employees, suppliers and investors (Andriof & Waddock, 2017). Stakeholders of the company have been arranged based on the level of interest and power. The strategy of acquisition by the company is not acceptable to the suppliers of the organisation as the acquisition of the other telecom company means that the existing suppliers would lose their value. The existing suppliers of Vodafone would lose their bargaining power as the company would have more availability. However this would not affect Vodafone as the suppliers have minimum power and interest in the business and hence required only monitoring (Corporate, 2019).
The employees of Vodafone are the stakeholder group with high interest and power and would be influenced by the organisational decision of acquisition (Bridoux & Vishwanathan, 2018). The employees of Vodafone would accept the corporate strategy of acquisition as they would be able to benefit from the global opportunities and challenges along with having chances of representing the organisation in other countries. The investors of Vodafone are the third set of stakeholders who have high power but low interest in the organisation. The investors of the company would accept the decision to the acquisition of Liberty Global as it would enable them to have more shares in the company and more scope of return from the abroad operations (IBC, 2019). However, the authorities of Vodafone would be required to ensure that they provide timely dividends and bonuses to those interested in gaining profits.
Feasibility:
The strategy of acquisition for Vodafone is feasible and can be implemented as the organisation has adequate financial resources available at its disposal. The organisation already dedicates a significant portion of the prophets for research and development along with infrastructure enhancement. The cost of the acquisition of Liberty global is €18 billion (Vodafone, 2020). Vodafone was required to ensure that they have liquid assets and funds available for investing. The organisation has completed the acquisition as it had sufficient assets and capital for supporting the purchase. However, the company was able to acquire the telecom enterprise by selling a part of its stock along with financing with a bank loan
Conclusion
This report is about the evaluation of the corporate strategy of Vodafone to acquire Europe Liberty global. The external analysis of Vodafone indicates that the organisation has the opportunity of political support for expansion along with technological advancements. Threats identified for the organisation indicate the availability of a substitute in the market whereas the strengths are the huge availability of human resources along with the number of outlets. Standard and similar network infrastructure is the weakness of Vodafone.
Appendix
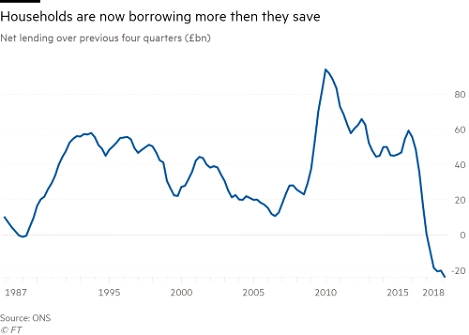
Appendix 1
Figure 1: UK lending.
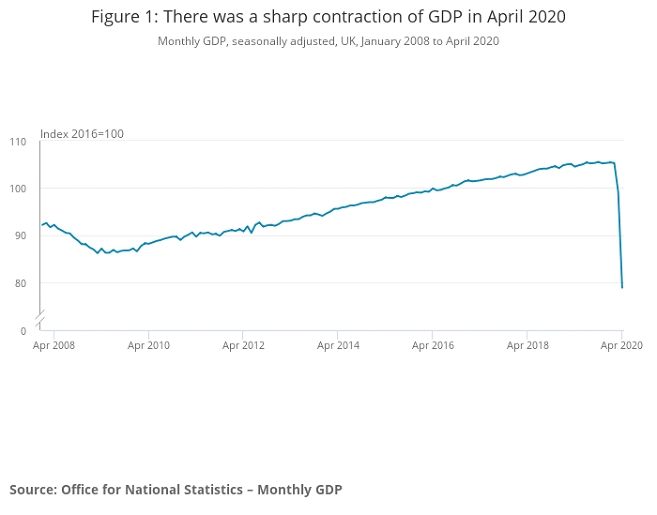
Appendix 2
Figure 2: UK GDP.
Appendix 3
Figure 3: Resource based View.
Appendix 4
Figure 4: Vodafone employees in UK.
Frequently Asked Questions
To develop a strategic report, start by defining the objective, conducting thorough research, analyzing data, identifying key insights, and formulating strategic recommendations. Organize the report logically and effectively communicate findings to stakeholders.